Even a perfectly performed breast augmentation can be ruined by a complication known as capsular contracture. To understand this process it is best to discuss the Baker classification.
- Soft in feel.
- Firm in feel, but no anatomic distortion.
- Breast feels firm and there is visible evidence of anatomic distortion.
- Breast feels firm, painful and there is anatomic distortion.
Whenever any foreign body is implanted in the body, it responds by forming scar tissue around it. The scar tissue is called a capsule in breast augmentation. Most implants remain soft and natural, but if a capsule forms around the implant, the breast can feel hard and look and feel unnatural. It can be so severe that it can cause implant malpositioning and pain. The cause of capsule contracture is not known, but certain risk factors can contribute.
RISK FACTORS:
- Previous hematoma.
- History of smoking.
- Placement above muscle.
- Infection.
The treatment ranges from massage and medications to revisional surgery.
NONSURGICAL TREATMENTS:
- Breast displacement exercises.
- Medications. Both herbal medicines, particularly medication known as milk thistle have been used to treat capsules. A asthma medicine known as Accolate or Singulair have been shown to have some benefit in capsule contracture although they are not FDA approved for that indication.
SURGERY FOR CAPSULE CONTRACTURE: Closed capsulotomy. This is mentioned for historical purposes only. The process of squeezing the implant to break the capsule is no longer accepted because of the trauma unknown to be implant. Today, only open procedures are accepted.
CAPSULOTOMY: It is better to wait at least six months prior to any revisional surgery for capsule contractures since many will resolve on their own. Capsulotomy requires complete release encasing scar tissue by cutting the base of the capsule as well as radial cuts. Improvement is immediate, but may take months to achieve symmetry.
CAPSULECTOMY: This is the process of completely removing the capsule or scar tissue. In my experience this is only necessary when there is a calcified capsule present and the majority capsules only release is required.
Even with a successful revisional surgery, there is no guarantee that the process will not reoccur. The recurrence rate is very high at 20-25% and can be frustrating for the patient and surgeon.
RIPPLING: Rippling is the most common complication of breast augmentation surgery. There are two types:
- Visible, where actual folds of the implant can be visible through the skin.
- Palpable, means although it may not be visible, when you touch the breast, there is a bag like feel. Both of this can be exaggerated by changing position of the body. Repair depends on the type of implant and its position. If a saline implant is placed then changing to a gel implant may fix the problem since silicone implants ripple less than saline. As a general rule, implants placed under the muscle ripple less than above. The worse case scenario is when a silicone implant is under the muscle and rippling is still present. This is usually seen in very thin women. One option would be to transfer fat to the breast for better coverage.
This is a 62 year old woman who developed early capsular contracture. You can see right breast appears smaller and much higher. After 4 months she was taken to surgery and a capsulotomy performed and 1 month after marked improvement. 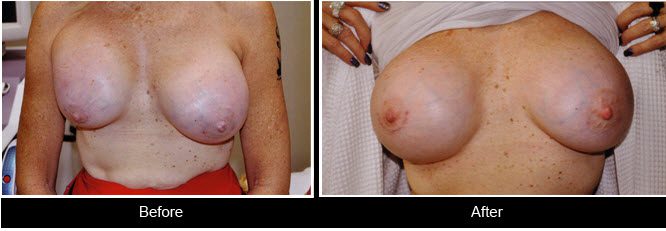
This 38 year old woman underwent breast augmentation but after 1 year her right breast became hard and painful. Capsule release was performed and improvement was evident. 4 years later her breast remains soft and natural.
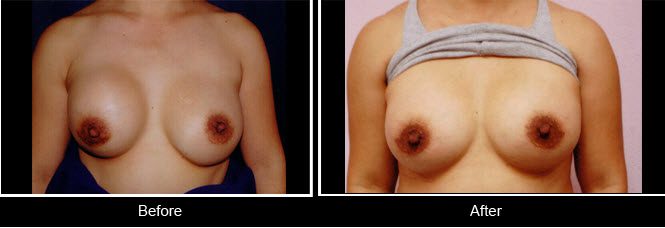
This 45 year old woman present after having breast augmentation 5 years ago. The left breast had become extremely hard and raised. After performing a left capsulotomy the problem was fixed.

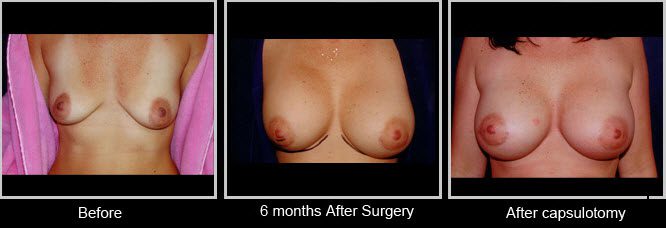
This 29 year old female developed early capsular contracture. This first picture shows preoperative breast. You can see the right breast is higher than the left. After surgery her right implant remained high. After 6 months it remained that way and capsulotomy done and after surgery you can see the marked improvement.
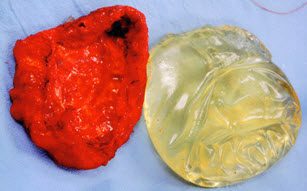
This shows an example of a capsule. This patient had a capsulectomy and the implant and encasing capsule are shown